Section: New Results
Automated Healthcare: Facial-expression-analysis for Alzheimer's Patients in Musical Mnemotherapy
Participants : Antitza Dantcheva, François Brémond, Philippe Robert.
keywords: automated healthcare, healthcare monitoring, expression recognition
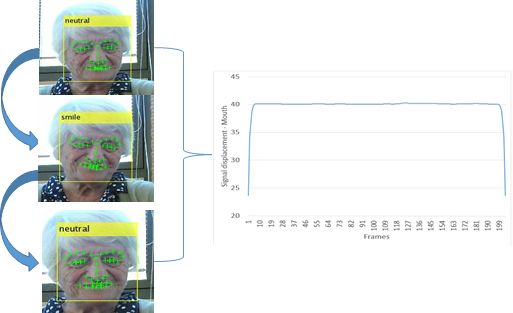
In this work we seek to apply computer vision towards increasing the life quality of patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD), and particularly in applying computer vision towards interventions to delay functional decline and to decrease the burden of the most disturbing behavioral symptoms. Towards this we design a smart interaction tool, that "reads" emotions of AD patients. This approach is becoming necessary now, because the increasing prevalence of chronic disorders and its impact on functional decline is challenging the sustainability of healthcare systems. Firstly, we have assembled a dataset of video-sequences acquired in the Alzheimer's Disease - clinique Fondation GSF Noisiez. Multiple patients and sessions have been captured during musical mnemotherapy. We then have annotated several sequences per one of four facial expressions, that occur in the recorded dataset including: neutral, talking, smile and sad. We then proceed to classify these expressions for 10 patients based on two approaches, that we study individually, as well as fused. The first approach contains face detection, facial landmark localization and signal displacement analysis for different facial landmarks, which are ranked based on categorization-pertinence, fused and classified into one of the four expression-categories (see Figure 11 ). In the second approach, we use face detection, eyes-detection, face normalization and HOG-features, which we classify into one of the four expression-categories.
|
The here used real-world-data challenges, as expected, all utilized computer vision algorithms (from face detection - due to no constraints of pose and illumination, to classifiers - due to a large intra-class-variation of facial expressions). Nevertheless, we obtain promising results that we envision improving by analyzing 2D and depth, as well as infrared data.